To turn things around, the education system needs to put in a place the kind of learning that will move people ahead of the technology of modern times.
That, said Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) director for Education and Skills Andreas Schleicher, is about knowledge, skills and mindsets.
In the era of generative artificial intelligence (AI) such as ChatGPT, he said teaching the young how to frame questions, navigate ambiguity and manage complexities, instead of teaching them the answers, is of utmost importance.
“We know how to educate second-class robots – people who are good at repeating what we tell them but the kinds of things that are easy to teach and easy to test have also become easy to digitise and automate,” he said.
Drawing on an OECD study that tracked the extent to which AI could surpass typically gifted humans in education, he noted a clear improvement in the performance of generative AI in just one year in the Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) (see infographic).
“You can see AI is advancing at a breathtaking pace. We need to accelerate our progress,” warned Schleicher, who leads the team that oversees PISA.
Creativity, he asserted, is one of the most central resources in the 21st century that education can foster to help people grow in their competence.
“If you want your kids to be creative, you have to give them space to experiment. When they experiment, they take risks and if they take risks, they make mistakes. If our education systems do not help students learn from and with mistakes, they are not going to be so creative,” he said.
Citing the teaching of science as an example, he said making students believe in scientific paradigms, giving them numerous exercises to rehearse, and testing them on whether they remember the answers have nothing to do with scientific enquiry.
“Scientific enquiry is not about reproducing the established wisdom of our times but about questioning it. And that is true for many subjects,” he said.
He added that rather than teaching students knowledge like physics and chemistry, educators should put more emphasis on helping them to think like scientists.
“That is going to be useful and sustainable. If we just teach fixed knowledge and skills, the risk they are going to become obsolete is quite high,” he said.
Speaking at the Educational Publishers Forum (EPF) Malaysia 2023, held virtually on Nov 22 last year, he added that learning literacy is no longer about extracting knowledge from prefabricated text; it’s about constructing knowledge.
“Instead of repeating and reproducing what you learn, you need to learn to question what you see, and triangulate different information. They are very different skill sets,” he said.
He added that students must have the capacity to see the world in different lenses and appreciate different ways of thinking.
Pointing to the massive rise in the “wisdom of the crowds”, where a large number of people put their ideas into the mix on social media, Schleicher also emphasised the need for students to be equipped with digital navigation skills.
“In many countries, the majority of 15-year-olds are born into this digital world but they are not digital natives.
“You will not become automatically skilled – education needs to invest in this,” he said, adding that the ability to distinguish fact from opinion and integrate different information sources is the kind of skill needed to make use of the digital world.
Nurturing a growth mindset, according to Schleicher, is another focal point of importance to help students forge ahead.
“The mindset we create among students is an incredibly important predictor for their willingness to engage with new problems and address challenges.
“Education systems that develop students’ growth mindset tend to also excel academically, while those that have a fixed mindset typically show a lower academic performance.
“If students have a growth mindset, it’s a mirror of how they have been educated,” he said.
Students with a growth mindset, he explained, know that if they invest effort, they can overcome barriers whereas those without it believe that success is largely about the intelligence they inherited and there is nothing they can do about it.
In fact, he continued, the growth mindset is needed at every level of the education system, including policymakers, teachers and publishers.
He added that one’s willingness and capacity to learn, unlearn and relearn will also be essential.
“In today’s world, you have to learn for jobs that have not yet been created, to use technologies that have not yet been invented, and to solve social problems you cannot yet imagine.
“So, having a willingness to engage in the novelty, and to give up some of the favourite beliefs, knowledge and skills in order to acquire new ones, is absolutely essential – that’s a real test for education today,” he said.
Themed “Developing 21st Century Students: Policies, Strategies & Educational Materials”, the EPF Malaysia 2023 was organised by the Malaysian Book Publishers Association.
Calls for edu reforms in M’sia
Less volume, more depth
Malaysia has put very interesting reforms on track but there can be less emphasis on the volume of content – Malaysian students learn a lot of things. Instead, place more emphasis on depth and diverse ways of thinking. That is the most important transition the modern world will require for students in Malaysia.
Learning environments can be more student-oriented and teachers can go beyond the instructional component and become better coaches and mentors to their students – that’s very important to mediate the impact of social background.
Engage teachers in more collaborative professional development. You need to get teachers in a space where they also become lifelong learners.
– OECD director for Education and Skills Andreas Schleicher
Strengthen school curriculum
The curriculum is by far the most important ingredient in determining what students are able to do at the end of their schooling.A fantastic teacher with a terrible curriculum is going to have a hard time ending up with successful students. And a teacher who is struggling is going to be supported by a terrific curriculum, so all teachers benefit from a strong curriculum. It’s something that policymakers should be reviewing on a regular basis. There is good data worldwide. We’re leaving a lot of good ideas on the table by not paying attention to what other folks are doing.
– University of Virginia, United States, psychology professor Dr Daniel Willingham
Ensure quality content
You can have highly-trained teachers teaching in classrooms with the most up-to-date devices and software but if the content being taught is second-rate or worse, then students will not get the education they deserve and your country will be left behind. If we want to reduce inequalities, then high-quality resources produced by professional educational publishers and adapted to deliver the government’s curriculum is what will guarantee progress.
– International Publishers Association president Karine Pansa Focus on leadership
We need to review our curriculum assessment and pedagogical approach. First, the Education Ministry (MoE) should collaborate with stakeholders to reassess the curriculum. Second, it should redefine the role of teachers. Our teachers are imparting knowledge that can be obtained online. Allow teachers to learn, unlearn, relearn, and be mentors and facilitators. The focus should be on leadership as stated in the Malaysia Education Blueprint (MEB) 2013-2025.
– Malaysian Association for Education president Datuk Satinah Syed Saleh
Decentralise the MoE
–
UCSI University architecture professor Prof Dr Mohd Tajuddin Mohd Rasdi
Address shortfall
Our National Education Philosophy is clear about producing holistic students in four aspects: intellectual, physical, emotional and spiritual. But how well we are implementing this in classrooms is something we need to address. The MoE needs to engage regularly with stakeholders.We have to prioritise our initiatives. For example, we are not spending enough on providing professional development opportunities for teachers, even though it was recognised in the MEB.
– University of Cyberjaya and Infrastructure University Kuala Lumpur adjunct professor Prof Datuk Dr Rajendran Nagappan
Replicate trust school model
The Trust Schools Programme, launched by Yayasan Amir and the MoE in 2010, came up with a model to transform teacher pedagogy skills underpinned by cultural change. It entails the schools shifting from a teacher-centric to a student-centric approach, and from teaching to the test to creating a positive learning environment that unleashes the potential of each student.We have 94 trust schools across Malaysia, involving at least 10,000 teachers and benefiting more than 200,000 students. The MoE has the intention to replicate the model but hasn’t caught up yet.
- LeapEd Services chair Shahnaz Al-Sadat Abdul Mohsein

TO improve performance in mathematics and science, educators and learning materials need to transmit excitement of the subjects to students.
Referring to the Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMMS) 2019, International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement (IEA) executive director Dr Dirk Hastedt said students who liked the subjects scored significantly higher than those who didn’t.
In fact, the over 100-score point difference translated to more than a year of learning.
“It’s very important that students like learning these subjects,” he stressed, adding that learning materials should be designed to engage both boys and girls to narrow the gender gap seen in TIMMS 2019, where girls outperformed boys in many countries, including Malaysia.
Hastedt also said students’ self-confidence in mathematics and science strongly correlates with their achievement, with more than a year of learning separating those with confidence from those without in the same study.
“What we can see from our data is that learning materials need to be targeted and supported by positive attitude to these subjects.
“We need students with a ‘can do’ attitude,” he asserted.
He added that it is important to have prerequisites such as language mastery.
“From our Progress in International Reading Literacy Study (PIRLS), we can see an increasing percentage of boys struggling with language.
“If you don’t have language capacity, it’s more difficult to learn mathematics and science,” he said.
Other strategies Hastedt recommended for improving student performance include incorporating software tools in learning and providing support for underprivileged students.
“Some students may understand better when using learning software managed by teachers. This enables more individualised learning,” he said.
However, he emphasised that this requires not only the availability of computers but also the presence of software administrators and technical support in schools – more importantly, teachers trained in using digital devices efficiently in teaching.
He also said digitalised instruction requires more than just transferring paper materials into a digital format.
“New digital materials that are engaging and helpful need to be developed. It requires a support structure and teachers need to be trained to use the software and help students learn in a digital environment,” he said.
Hastedt added that it’s important to move international assessments to the same digital format used in teaching and learning.
Cognisant of the need to keep up with the times, the IEA, which conducts TIMMS, introduced its fully digitised version, eTIMMS, in its 2023 cycle, he shared.
“We have to recognise that students today engage with the digital world through digital media and mobile phones. They find this more engaging than traditional methods. We have to keep up with the interest,” he said.
Hastedt, however, cautioned that digitalisation could exacerbate gaps in learning.
Citing a study on digital competencies, he said the gaps between different socioeconomic groups are huge – “larger than for reading, mathematics and science”.
“Digital competencies are not always well covered in countries’ curricula, and teachers sometimes don’t teach these competencies,’ he said.
A focus, he emphasised, is needed on the most vulnerable student groups as early as possible, starting from kindergarten or the early grades.
Citing a TIMMS study that highlights a difference of more than one year of learning between students from disadvantaged and affluent backgrounds, he noted that in Malaysia and many other countries, students with challenging socioeconomic backgrounds struggle more often with mathematics and science achievements.
“A focus on supporting students from lower social economic background would not only benefit these students, but also enhance the overall achievement of all students due to the positive peer effect.
“And if teachers can concentrate on all students because of a good level of knowledge, that benefits all students in the country,” he concluded.
Related posts:


















 Looking ahead: Malaysia’s Institute for Medical Research is currently working on a few Covid-19 vaccines. — SAMUEL ONG/The Star
Looking ahead: Malaysia’s Institute for Medical Research is currently working on a few Covid-19 vaccines. — SAMUEL ONG/The Star












 Will Uncle Sam be able to continue deceiving the world in terms of investigation into COVID-19 origins?
Will Uncle Sam be able to continue deceiving the world in terms of investigation into COVID-19 origins?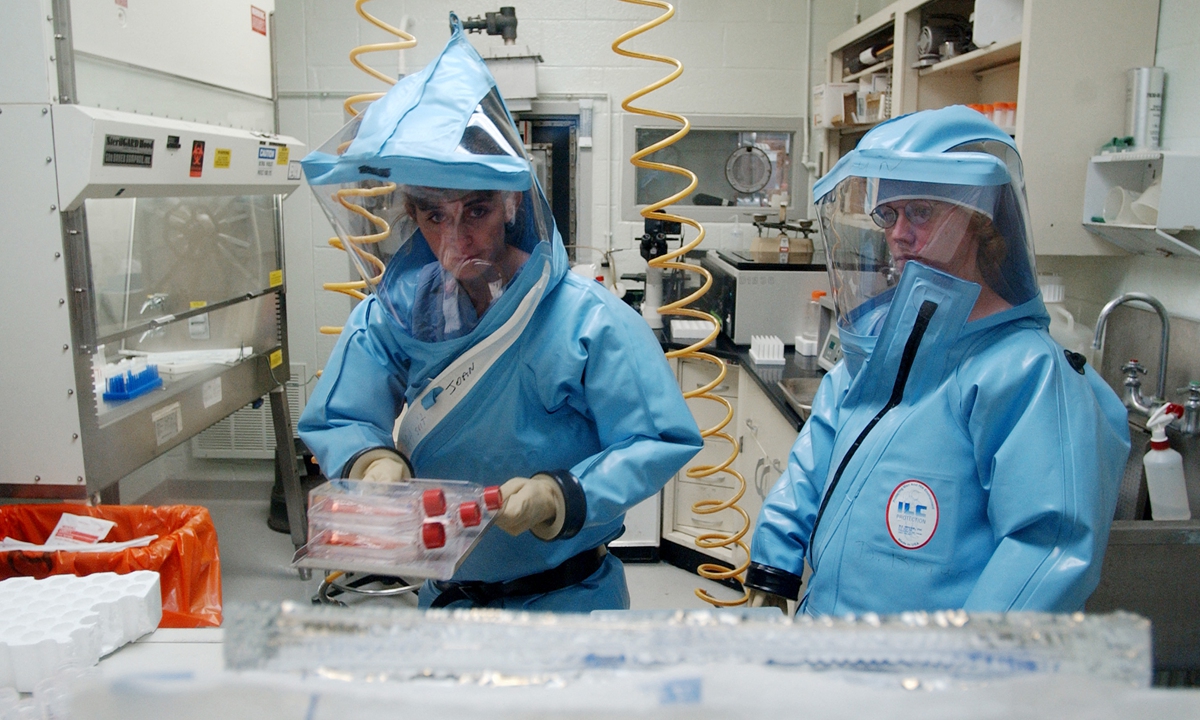 Research personnel work inside the bio-level 4 lab at the USAMRIID at Fort Detrick on September 26, 2002. Photo: AFP
Research personnel work inside the bio-level 4 lab at the USAMRIID at Fort Detrick on September 26, 2002. Photo: AFP






