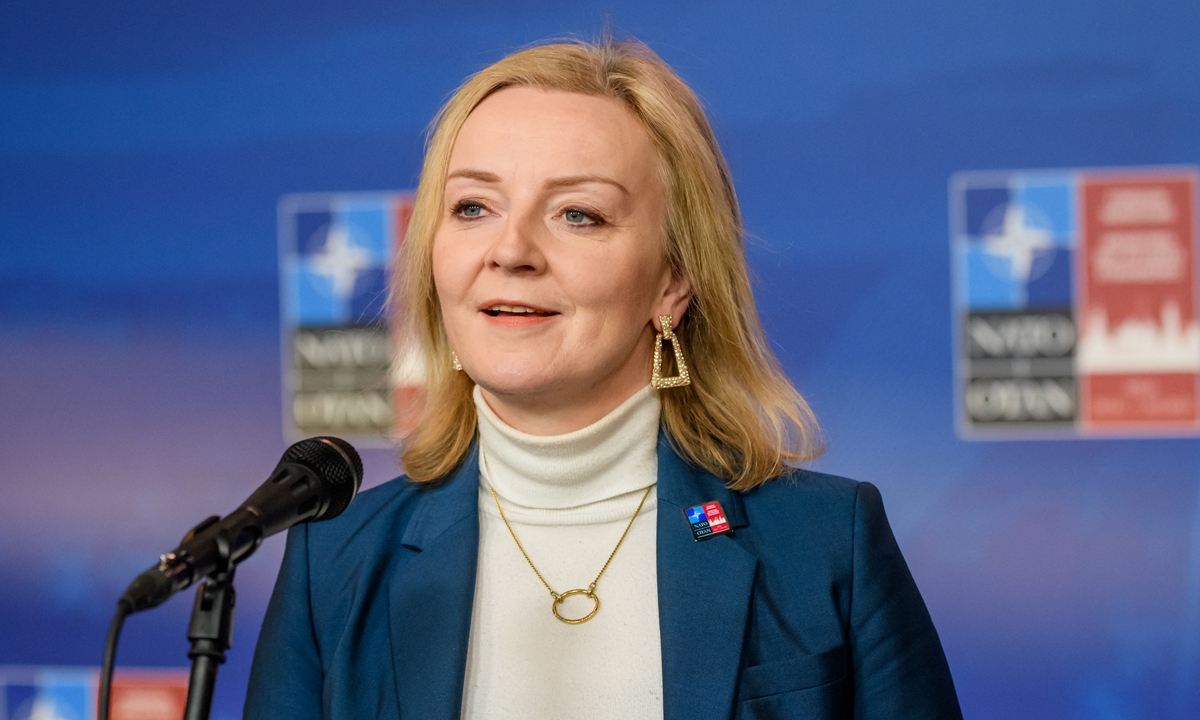
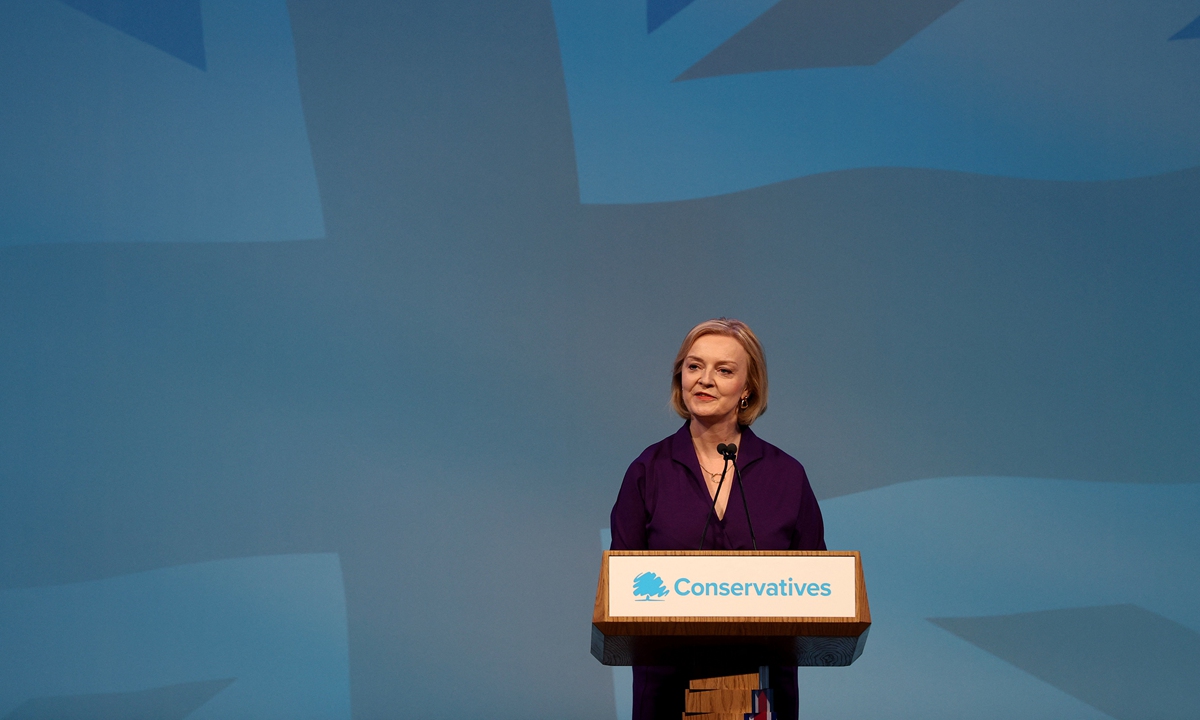
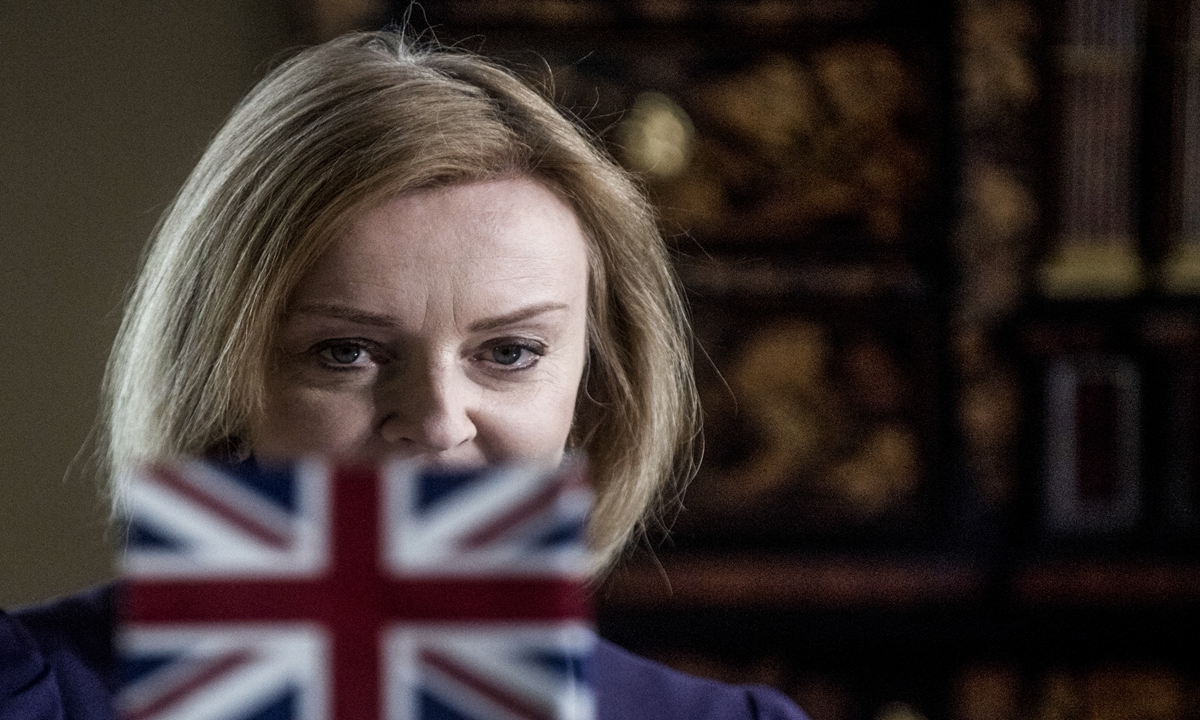
Liz Truss delivers a speech at an event to announce the winner of the Conservative Party leadership contest in central London on September 5,2022. Photo: AFP
Liz Truss is the new British Prime Minister. She beat her Conservative rival Rishi Sunak by tacking strongly to the right. No doubt the fact that she is white, and Sunak is brown, was also a major factor for the 170,000 overwhelmingly white Conservative Party members who voted. If Truss is to be taken at her word, she will be the most right-wing prime minister since Margaret Thatcher in the 1980s.
Each of the last four Conservative prime ministers has been more right-wing than their predecessor: in chronological order, David Cameron, Theresa May, Boris Johnson, and Liz Truss. Truss wants to cut taxes, doesn't like the state, is hostile to redistribution, believes in trickle-down economics (that feathering the nests of the rich will ultimately help the poor), and is an anti-China hawk. In being true to her beliefs, however, she faces a gargantuan problem. She is confronted with the worst economic crisis of any British prime minister since 1945. It is impossible to find any good news on the economic front. As a result of the war in Ukraine, the price of natural gas, which is the main source of domestic heating, is five times what it was a year ago and is predicted to carry on rising steeply. Without state intervention to hold down energy prices, around half the population will this winter be impoverished. Inflation, which for most of this century has been at around 2 percent, is already at 11 percent, and is predicted to rise to 20 percent. Interest rates, which have similarly been very low, are rising rapidly, meaning much higher mortgage payments for homeowners. The Bank of England forecasts that the country will go into recession towards the end of this year, and some believe that it will continue until 2024. With inflation now in double figures, workers are finding they are facing wage increases that are less than half the increase in prices: as a result, they are confronted with the prospect of sharply declining real wages over the next several years. There is growing industrial unrest which is likely to become increasingly widespread over the next year. This is not just a short-term problem. Real wages are now just below the level they were in 2007, on the eve of the Western financial crisis. In other words, the British economy has been stagnating for the last 15 years and in the process has been falling behind its near neighbours Germany and France. One major think-tank is predicting that over the next two years Britain will experience the largest fall in average real incomes for over one hundred years. It is inconceivable that Truss can tackle this nightmare scenario by cutting taxes, rolling back the state, and turning a blind eye to the poorest sections of the community. This will require state intervention and redistribution on the scale of the COVID-19 crisis in 2020, otherwise the Conservative Party will surely lose the next general election in 2024. Truss faces a major dilemma: take the right-wing ideological route and court electoral disaster or follow a pragmatic road and swallow her ideological principles. Even before the coming economic tsunami, there was a mood of frustration and dislocation, a feeling that the country no longer worked properly. Far from ushering in a new era of prosperity and efficiency, Brexit has become synonymous with labour shortages in many parts of the economy. This has been accentuated by the impact of COVID-19 which continues to disrupt the economy, most obviously in the form of chronic labour shortages in many sectors. Britain's most-loved institution, the National Health Service, is now on life-support, a result of being starved of money for many years and an increasingly chronic shortage of staff. It is important to emphasise that Britain is now in a much inferior position than it was in 1979 when Thatcher first came to power. This is a weakness it shares more generally with the West and especially Western Europe. The Soviet bloc aside, the West for the most part dominated the world during the 1980s. Its influence and hinterland, however, are now much reduced because of the rise of China together with that of the developing world. A topical example will suffice to illustrate the point. Is the present spike in oil and gas prices, which are costing Western Europe dearly, a permanent or temporary phenomenon? It looks very likely that it will be the former, that Western Europe will be permanently disadvantaged, because Russia has found new markets, notably India and China, for its oil. Western Europe enjoys less economic power in the world and its room for manoeuvre has contracted. This is what being part of the declining part of the world means.Finally, what will Truss mean for Britain's relations with China? There is no reason for optimism. Truss thinks of herself as a cold war warrior. She has strongly hinted that China will be designated a "threat" to national security and treated in the same way as Russia. The golden age in the relationship between Britain and China came to an end around five years ago and there is precious little chance of it returning for a long time to come.
 By Martin Jacques
By Martin Jacques
| Born | 1945 (age 73–74)
Coventry, England, Great Britain, U.K
|
|---|---|
| Nationality | British |
| Education | King Henry VIII School, Coventry |
| Alma mater | University of Manchester (B.A.) University of Cambridge (PhD) |
| Occupation | Editor, academic, author |
| Website | MartinJacques.com |
The author was until recently a senior fellow at the Department of Politics and International Studies at Cambridge University. He is a visiting professor at the Institute of Modern International Relations at Tsinghua University and a senior fellow at the China Institute, Fudan University. Follow him on twitter @martjacques. opinion@globaltimes.com.cn